Introduction
Regulations: Art. 50 Law PIT
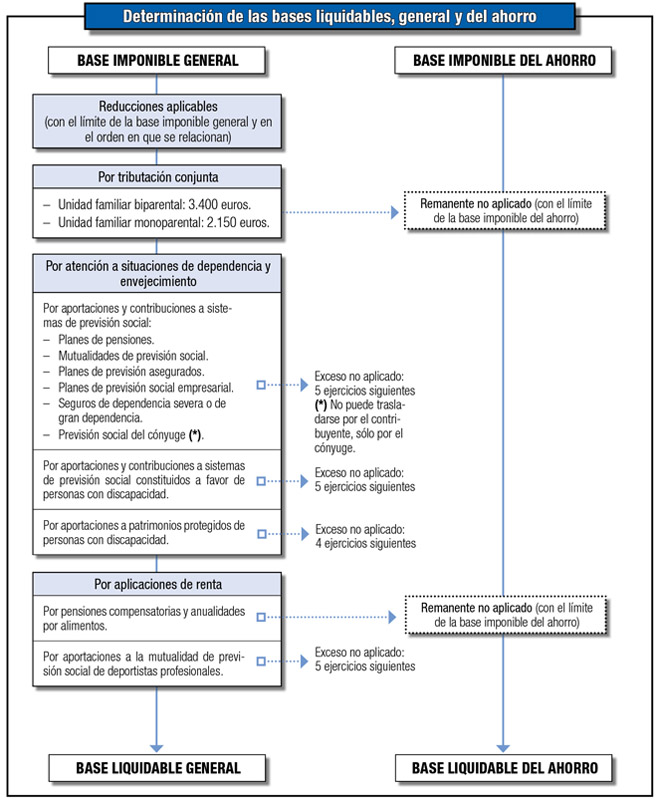
Once the general tax base and the savings taxable base have been determined, as a result of the income integration and compensation procedure discussed in the previous chapter, the general taxable base and the savings taxable base must be determined.
The general taxable base is the result of applying the following reductions to the general tax base, exclusively and in this order, without it being able to result in a negative result as a consequence of said reductions:
-
Reduction for joint taxation (art. 84 Law PIT).
-
Reduction for contributions to social security systems (art. 51 Law PIT).
-
Reduction for contributions to social security systems established for people with disabilities (art. 53 Law PIT).
-
Reduction for contributions to protected assets of people with disabilities (art. 54 Law PIT).
-
Reduction for compensatory pensions (art. 55 Law PIT).
-
Reduction for contributions to the social security mutual fund for professional athletes (Additional Provision of the Eleventh Law) PIT).
The taxable savings base is the result of decreasing the taxable savings base by the remainder, if any, of the reductions for joint taxation and compensatory pensions, without it being able to be negative as a consequence of such reductions.
The process of determining these two magnitudes can be represented schematically as follows: